|
Description
Simply put, a database is a collection of data. An appointment book
is a database of appointments; a diary is a database of personal notes;
an address book is a database of addresses; a library catalog is a database
of book information.
With the
vast amount of information bombarding us today, it is important to organize
and categorize all the data we accumulate. Having computerized databases
of our data makes it easy to do so. Browsing, searching, sorting, and
reporting become trivial tasks.
Tables
Data in a database is grouped into database objects called tables. A
table is a database structure that contain records of data having common
fields or attributes. Tables are given unique and meaningful names to
distinguish them from other tables. For instance a table called 'Customers'
would contain records about customers. Each customer will have a record
of data in the table.
Fields
Each record in a table is split into different attributes called fields
or columns. Each field is given a unique name within its table to distinguish
it from other fields. For instance, a 'Customer' table record will probably
contain the fields 'Name', 'Telephone', and 'Address'. Each field is
of a particular data type.
Data
Types
When a field is created, it is created as a field of a particular data
type. The field's data type specifies what kind of data is allowed to
be stored in that field, how the field will be displayed, and how the
field can be used in calculations. The data types supported by QuickModules.com
are the following:
|
|
- Notes
- List Box
- Radio Button
|
- E-Mail Link
- URL
- Image Link
|
- Text Formula
- Numeric Formula
- Date Formula
|
Click
here for a detailed description of each data type.
In addition to the above
data type, QuickModules.com also supports sub-tables or nested tables.
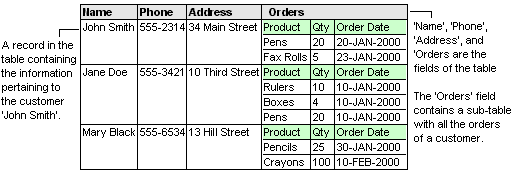
Sub-Tables
A sub-table (also known as a nested table) is a complete table stored
as a value of a field in a record. This is useful for storing multiple
data associated with a particular record. For instance, a record of
table 'Customer' might have the sub-table 'Orders' which contains all
the orders for that customer.
Example
The following 'Customer' table contain infomation about customers:
See
Also
Working With Data
|
